Pages
16
-3-
Orfield, Gary + Chungrei Lee,
"Brown at 50: Kiy's Dream or Plessy's Nightmare?" The Harv. Civ. Rts. Proj. (Jan. 2004)
[left hand margin] Asians most integrated
@1: "U.S. schools are becoming more seg. in all regions for both Afr. Am. & Latino students. We are educating a victory over any at a time when sch. across the nat are becoming increasingly segregated." (largest backward movement in St. 'cus it led moved far that forward)
Ne merdin of Latinos until 19 yr after BRown; never any signifigence of desy for Latinos.
@ 2 All most major of intensely sg. minor scl. fad cond of conceracted fortly
@3 "There last here no signif policy intiavites to foster disg schooling the thirty yrs. Most recent initiatives in assessment, accotentabile & choice purport to solve the probles of minot children while ignoring a ever intersifying seg."
@ 8 re Grutter v. Bollinger: " Nothing so [position about the complelling necessity of iinterracial educ. has her said by 76 S. Ct. for three decades."
@ 16. "The period of 76 c.r. rent prod rent days in So. sch. from 1964 to 1992 as Cong and 76 Johnsn Admin. committed themselved to as unprecidented effort to enford cov ts is 76 Sout"
@17 '64-70% of tHks is al schools incr. monethor 14-fold!
17
-4-
requires gov't action & favorable cr. ralings - both of the reg. will of 76 people.
at 23: Helen Brown decided, 70& of college educated Amer. sided w/[?]2
id: Jack Guntry - "The other side's [illegible] talked about federalism, separ. of plans, taxtualism. Ours talked about reight and wrong."
And the [illegible]. Brown over about [illegible] not [illegible] for 19 yrs Asian most integrated. Brown was about what LBJ called "the one huge wrong of the American Nation (Speech commence Howard
18
Brown@50 Fulfilling the Promise
Howard University School of Law
HUSL-Yale Brown@50 Joint Conference
The Legacy of Brown v. Board of Education Reflections on the Last Fifty Years 1954-2004
| HUSL Events | Outside Events | Chronology | Cases & Other Law | Education & Other Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HUSL Home | HU Home | Brown@50 Home | Contacts | New Photos |
This chronology includes many items of general importance in the long march to equality, but it is not intended to be complete. The first item fairly closely related to Brown is a 1849 Massachusetts case in which the Massachusetts Supreme Court stated that separate but equal was permissible. The Massachusetts legislature overturned that decision six years later. Entries become more closely related to Brown with Plessy in 1896 band with many events following the Brown decision in 1954.
With respect to 20th and 21st century events, this particular chronology emphasizes law, and most particularly cases. Most of the cases noted in the 20th and 21st century are either important antecedent cases showing the development of the ideas leading to Brown or are important cases which show the evolution of and application of principles after Brown like the idea of affirmative action.
We are in the process of updating and annotating the chronology to make it a more valuable resource for students and researchers. This chronology builds on the work of many others, of course, as will be noted by the links to various authorities. The compilation of this timeline is primarily the work of Prof. Steven D. Jamar, and HUSL librarians Tracey Woodward and EIleen Santos. Many others have made helpful suggestions as well.
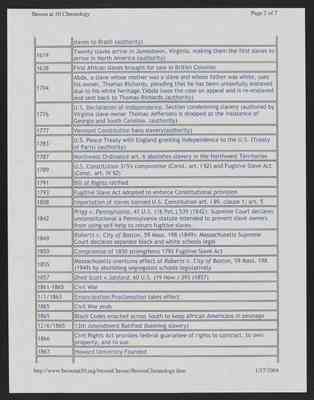
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1501 | Spain approves the importation of Africans to be enslaved in the Western Hemisphere (authority) |
| 1502 | First African slaves arrive in the Western Hemisphere on a cargo ship from Portugal (authority) |
| 1522 | African slaves revolt for the first time on a sugar mill in the Dominican Republic (authority) |
| 1562 | England enters the slave trade -- Sir John Hawkins of Engladn imports 300 slaves to Brazil (authority) |
19
Brown at 50 Chronology Page 2 of 7
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| slaves to Brazil (authority) | |
| 1619 | Twenty slaves arrive in Jamestown, Virginia, making them the first slaves to arrive in North America (authority) |
| 1638 | First African slaves brought for sale in British Colonies |
| 1704 | Abda, a slave whose mother was a slave and whose father was white, sues his owner, Thomas Richards, pleading that he has been unlawfully enslaved due to his white heritage. Abda loses the case on appeal and is re-enslaved and sent back to Thomas Richards. (authority) |
| 1776 | U.S. Declaration of Independence. Section condemning slavery (authored by Virginia slave owner Thomas Jefferson) is dropped at the insistence of George and South Carolina. (authority) |
| 1777 | Vermont Constitution bans slavery (authority) |
| 1783 | U.S. Peace Treaty with England granting independence to the U.S. (Treat of Paris) (authority) |
| 1787 | Northwest Ordinance art. 6 abolishes slavery in the Northwest Territories |
| 1789 | U.S. Constitution 3/5's compromise (Const. art. I §2) and Fugitive Slave Act (Const. art. IV §2) |
| 1791 | Bill of Rights ratified |
| 1793 | Fugitive Slave Act adopted to enforce Constitutional provision |
| 1808 | Importation of slaves banned U.S. Constitution art. I §9, clause 1; art. 5 |
| 1843 | Prigg v. Pennsylvania 41 U.S. (16 Pet.) 539 (1842): Supreme Court declares unconstitutional a Pennsylvania statute intended to prevent slave owners from using self-help to return fugitive slaves. |
| 1849 | Roberts v. City of Boston, 59 Mass. 198 (1849): Massachusetts Supreme Court declares separate black and white schools legal |
| 1850 | Compromise of 1850 strengthens 1793 Fugitive Slave Act |
| 1855 | Massachusetts overturns effect of Roberts v. City of Boston 59 Mass. 198 (1949) by abolishing segregated schools legislatively |
| 1857 | Dred Scott v. Sanford 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857) |
| 1861-1865 | Civil War |
| 1/1/1863 | Emancipation Proclamation takes effect |
| 1865 | Civil War Ends |
| 1865 | Black Codes enacted across South to keep African Americans in peonage |
| 12/6/1865 | 13th Amendment Ratified (banning slavery) |
| 1866 | Civil Rights Act provides federal guarantee of rights to contract, to own property, and to sue |
| 1867 | Howard University Founded |
20
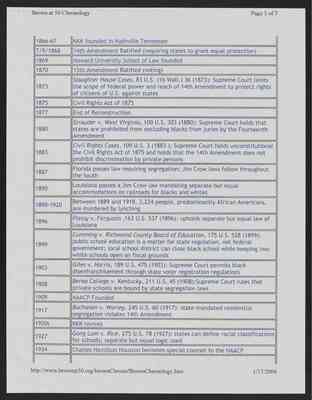
Brown at 50 Chronology Page 3 of 7
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 1866-67 | KKK founded in Nashville Tennessee |
| 7/9/1868 | 14th Amendment Ratified (requiring states to grant equal protection) |
| 1869 | Howard University school of Law founded |
| 1870 | 15th Amendment Ratified (voting) |
| 1873 | Slaughter House Cases, 83 U.S. (16 Wall.) 36 (1873): Supreme Court limits the scope of federal power and reach of 14th Amendment to protect rights of citizens of U.S. against states |
| 1875 | Civil Rights Act of 1875 |
| 1877 | End of Reconstruction |
| 1880 | Strauder v. West Virginia, 100 U.S. 303 (1880): Supreme Court holds that states are prohibited from excluding blacks from juries by the Fourteenth Amendment |
| 1883 | Civil Rights Cases, 109 U.S. 3 (1883): Supreme Court holds unconstitutional the Civil Rights Act of 1875 and holds that the 14th Amendment does not prohibit discrimination by private persons |
| 1887 | Florida passes law requiring segregation; Jim Crow laws follow throughout the South |
| 1890 | Louisiana passes a Jim Crow law mandating separate but equal accommodations on railroads for black and white |
| 1890-1920 | Between 1889 and 1918, 3,224 people, predominantly African Americans, are murdered by lynching |
| 1896 | Plessy v. Ferguson, 163 U.S. 537 (1896): upholds separate but equal law of Louisiana |
| 1899 | Cumming v. Richmond County Board of Education, 175 U.S. 528 (1899): public school education is a matter for state regulation, not federal government; local school district can close black school while keeping two white schools open on fiscal grounds |
| 1903 | Giles v. Harris, 189 U.S. 475 (1903): Supreme Court permits black disnefranchisement through state voter registration regulations |
| 1908 | Berea College v. Kentucky, 211 U.S. 45 (1908): Supreme Court rules that private schools are bound by state segregation laws |
| 1909 | NAACP Founded |
| 1917 | Buchanan v. Warley, 245 U.S. 60 (1917): state-mandated residential segregation violates 14th Amendment |
| 1920 | KKK revives |
| 1927 | Gong Lum v. Rice, 275 U.S. 78 (1927): states can define racial classifications for schools; separate but equal logic used |
| 1934 | Charles Hamilton Houson becomes special counsel to the NAACP |